728x90
Geometric Transformations
Geometric Transformation, $\mathbb{T}$
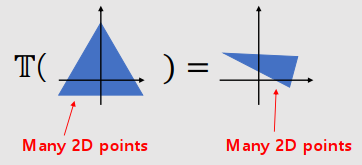
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function
- Geometric structure A → Geometric structure B
- A geo. structure is represented by a set of points or vectors in 2D o 3D in the general case.
2D Examples
Scaling
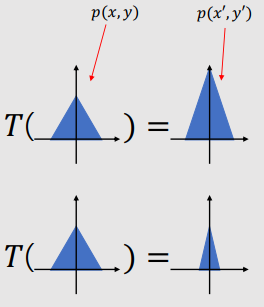 |
● Scale by 2 in the y-axis. → $S(1, 2)$ ▶ $x^{'} = x$ ▶ $y^{'} = 2y$ ● Scale by 0.5 in the x-axis. → $S(0.5, 1)$ ▶ $x^{'} = 0.5x$ ▶ $y^{'} = y$ ● Scale by $s_{x}$ and $s_{y}$ in the x and y-axis respectively. → $S(s_{x}, s_{y})$ ▶ $x^{'} = s_{x}x$ ▶ $y^{'} = s_{y}y$ |
Rotation
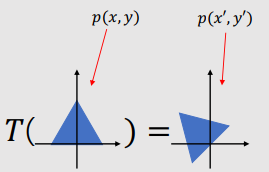 |
● Rotate by 45˚ about the origin. → $R(45˚)$ ▶ $x^{'} = cos(45˚)x - sin(45˚)y$ ▶ $y^{'} = sin(45˚)x + cos(45˚)y$ ※ Because of the Law of Cosine. ● Rotate by θ˚ about the origin. → $R(\theta)$ ▶ $x^{'} = cos(θ˚)x - sin(θ˚)y$ ▶ $y^{'} = sin(θ˚)x + cos(θ˚)y$ |
Translation
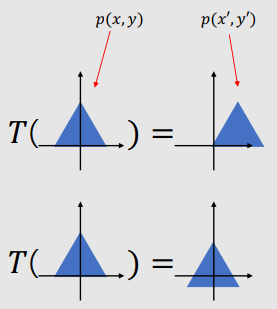 |
● Translate by 2 in the x-axis. → $T(2, 0)$ ▶ $x^{'} = x + 2$ ▶ $y^{'} = y$ ● Translate by -1 in the y-axis. → $T(0, 1)$ ▶ $x^{'} = x$ ▶ $y^{'} = y - 1$ ● Translate by $t_{x}$ and $t_{y}$ in the x and y-axis, respectively. → $T(t_{x}, t_{y})$ ▶ $x^{'} = x + t_{x}$ ▶ $y^{'} = y + t_{y}$ |
Composite Transformations(합성 변환)
Example 1
- Rotate by 45˚ about the origin, then scale by 2 in the y-axis.
- $R(45˚) → S(1, 2)$
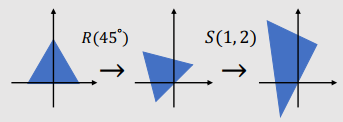
● $R(45˚)$
$x' = cos45˚x - sin45˚y$
$y' = sin45˚x + cos45˚y$
● $S(1, 2)$
$x'' = 1x'$
$y'' = 2y'$
▼
● $R(45˚) → S(1, 2)$
$x''' = 1·(cos45˚x - sin45˚y)$
$y''' = 2·(sin45˚x + cos45˚y)$
Example 2
- $R(45˚) → S(1, 2) → R(-45˚) → T(-1, 0)$
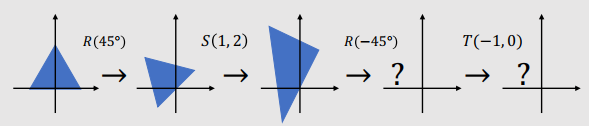
● $R(45˚)$
$x' = cos45˚x - sin45˚y$
$y' = sin45˚x + cos45˚y$
● $S(1, 2)$
$x'' = 1x'$
$y'' = 2y'$
● $R(-45˚)$
$x''' = cos(-45˚)x'' - sin(-45˚)y''$
$y''' = sin(-45˚)x'' + cos(-45˚)y''$
● $T(-1, 0)$
$x'''' = x''' - 1$
$y'''' = y'''$
▼
● $R(45˚) → S(1, 2) → R(-45˚) → T(-1, 0)$
$x'''' = cos(-45˚)·(1·(cos(-45˚)x - sin(-45˚)y) - sin(-45˚)·(sin(-45˚)x'' + cos(-45˚)y'') - 1$
$y'''' = sin(-45˚)·1·(cos45˚x - sin45˚y) + cos(-45˚)·2·(sin45˚x + cos45˚y)$
2×2 Matrix Form
- Scale by $s_{x}$ and $s_{y}$.
| $x' = s_{x}x$ $y' = s_{y}y$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} s_{x} & 0 \\ 0 & s_{y} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} $$ |
- Rotate by $\theta˚$ about the origin.
| $x' = cos(θ˚)x - sin(θ˚)y$ $y' = sin(θ˚)x + cos(θ˚)y$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} cosθ & -sinθ \\ sinθ & cosθ \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} $$ |
- Translate by $t_{x}$ and $t_{y}$.
| $x' = x +t_{x}$ $y' = y + t_{y}$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} t_{x} \\ t_{y} \end{bmatrix} $$ |
Questions
 |
|
3×3 Matrix Form (Homogeneous Coordinates(동차 좌표))
- Scale by $s_{x}$ and $s_{y}$.
| $x' = s_{x}x$ $y' = s_{y}y$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} s_{x} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & s_{y} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ |
- Rotate by $\theta˚$ about the origin.
| $x' = cos(θ˚)x - sin(θ˚)y$ $y' = sin(θ˚)x + cos(θ˚)y$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} cosθ & -sinθ & 0 \\ sinθ & cosθ & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ |
- Translate by $t_{x}$ and $t_{y}$.
| $x' = x +t_{x}$ $y' = y + t_{y}$ |
=> | $$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & t_{x} \\ 0 & 1 & t_{y} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ |
Composite Transformations
Example 1
- $R(45˚) → S(1, 2)$
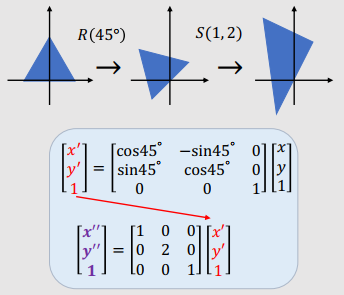 |
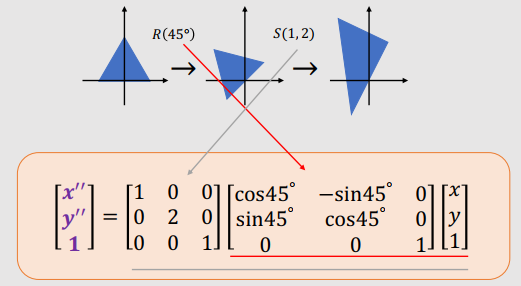 |
Example 2
- $R(45˚) → S(1, 2) → R(-45˚) → T(-1, 0)$

$$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} =
\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & -1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} cos(-45˚) & -sin(-45˚) & 0 \\ sin(-45˚) & cos(-45˚) & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} cos45˚ & -sin45˚ & 0 \\ sin45˚ & cos45˚ & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
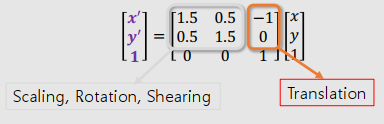
$ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 1.5 & 0.5 & -1 \\ 0.5 & 1.5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $
Ignoring the translation
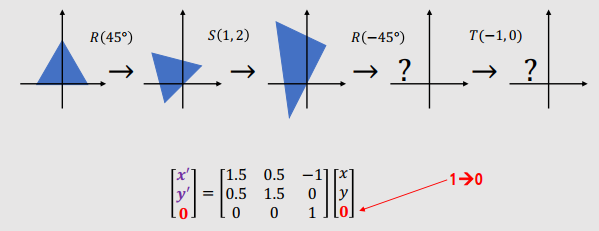
- Translation시키지 않고, Scaling, Rotation을 바꾸고 싶을 경우, 끝 부분을 0으로 바꿔주면 된다.
Summary
- 2D Transformation
- Scaling
- Rotation
- Translation
- Homogenous Coordinate(동차좌표)
- Allows to represent scaling, rotation and translation in a single matrix.
In 3D Space
Transformation in 3D Space (Homogeneous Coordinates)
| Transformation | Equations |
| 3D Translation |  |
| 3D Scaling | 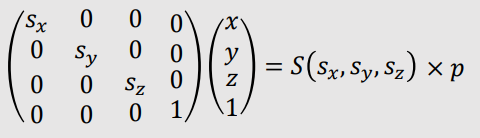 |
| Rotation | 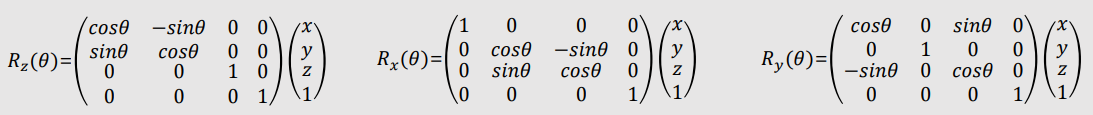 |
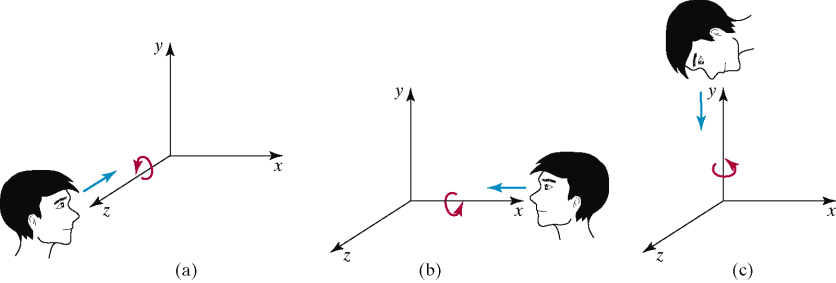
Transformations
① Linear Transformation(선형 변환)
| 2D Spaces |
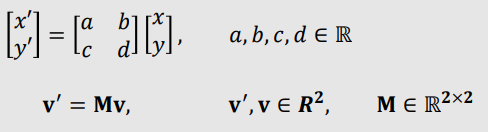 |
| 3D Spaces |
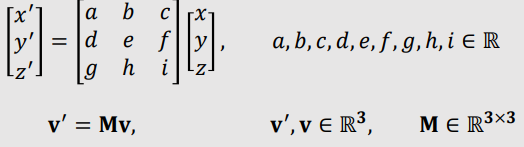 |
- A Linear Transformation $\mathbb{T}$ is a mapping between vector spaces.
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors.
- $\mathbb{T}: v → v', $ $v, v' \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$
- Linear Combination is invariant(불변한) under $\mathbb{T}$
- $\mathbb{T}(\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}v_{i}) = c_{0}\mathbb{T}(v_{0}) + c_{1}\mathbb{T}(v_{1}) + \cdots + c_{n}\mathbb{T}(v_{n})$
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors.
Examples of Linear Transformations
| 2D Rotation | |
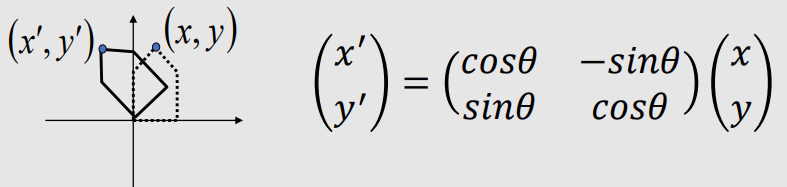 |
|
| 2D Scaling | |
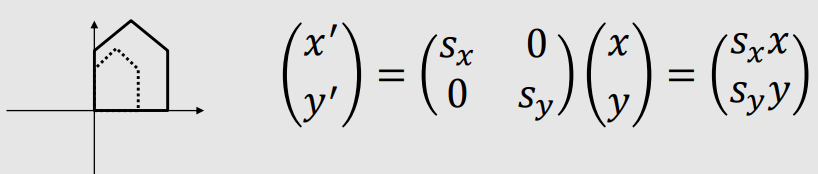 |
|
| 2D Shear | |
Along X-axis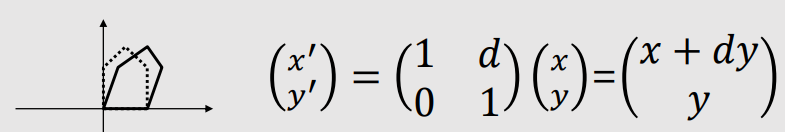 |
Along Y-axis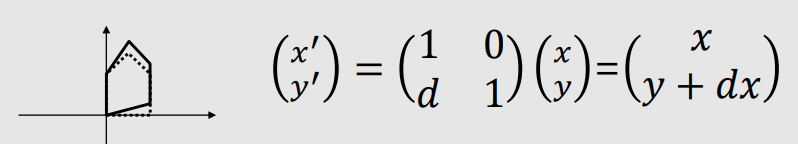 |
| 2D Reflection | |
Along X-axis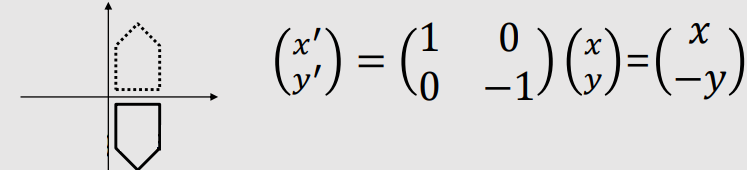 |
Along Y-axis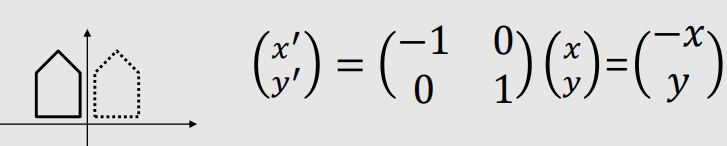 |
Properties of Linear Transformations
- Any Linear Transformation between 3D spaces can be represented by a 3×3 matrix.
- Any Linear Transformation between 3D spaces can be represented by as a combination of rotation, shear and scaling.
- Rotation can be represented as a combination of scaling and shear.
- A Linear Transformation maps lines to lines.
- A Linear Transformation maps parallel lines to parallel lines.
- A Linear Transformation preserves ratios of distance along a line.
- A Linear Transformation does not preserve absolute distances and angles.
② Affine Transformation(아핀 변환)
| 2D Spaces |
 |
| 3D Spaces |
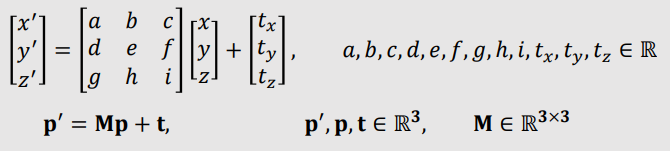 |
- An Affine Transformation $\mathbb{T}$ is a mapping between affine spaces.
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors, and points to points.
- $\mathbb{T}: v → v', $ $v, v' \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$
- $\mathbb{T}:p → p', $ $p, p' \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$
- Affine Combination is invariant(불변한) under $\mathbb{T}$
- $\mathbb{T}(\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}p_{i}) = c_{0}\mathbb{T}(p_{0}) + c_{1}\mathbb{T}(p_{1}) + \cdots + c_{n}\mathbb{T}(p_{n})$
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors, and points to points.
Homogeneous Coordinates
- Any Affine Transformation between 2D spaces can be represented by a 3×3 matrix.
- $\mathbb{T}(p) = \begin{pmatrix} M_{2×2} & T_{2×1} \\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} p_{2×1} \\ 1 \end{pmatrix}$
- Any Affine Transformation between 3D spaces can be represented by a 4×4 matrix.
- $\mathbb{T}(p) = \begin{pmatrix} M_{3×3} & T_{3×1} \\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} p_{3×1} \\ 1 \end{pmatrix}$
Affine Transformations (Homogenous Coordinates)
| 2D Spaces |
 |
| 3D Spaces |
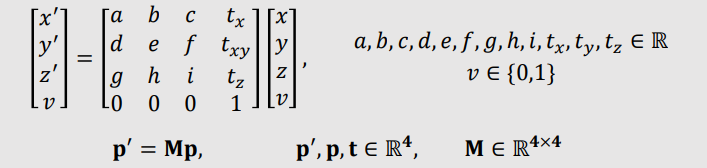 |
Examples of Affine Transformations
| 2D Rotation | |
 |
|
| 2D Scaling | |
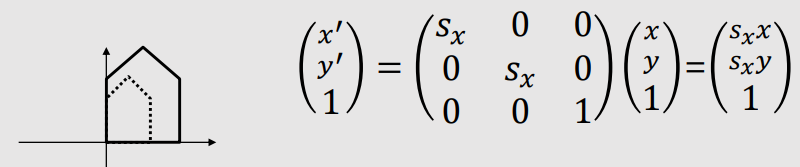 |
|
| 2D Shear | |
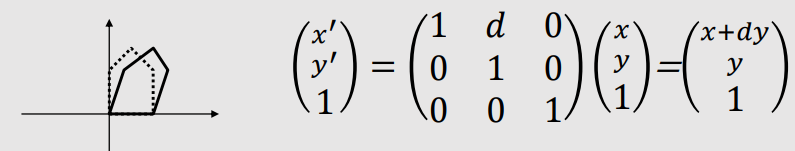 |
|
| 2D Reflection | |
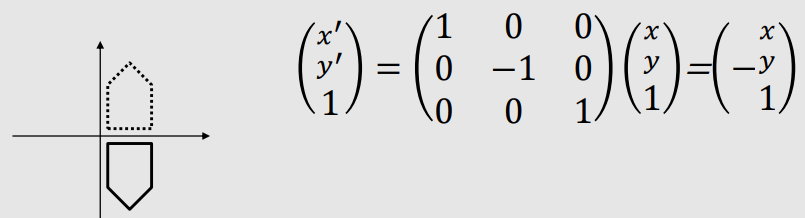 |
|
| 2D Translation | |
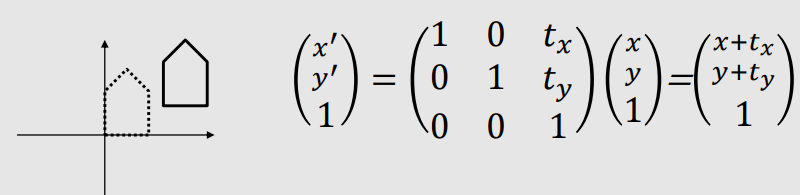 |
- 2D Transformation for vectors
- Translation is simply ignored.
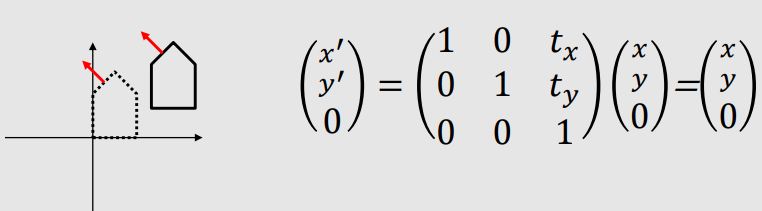
Properties of Linear Transformations
- Any Affine Transformation between 3D spaces can be represented as a combination of a Linear Combination followed by Translation.
- An Affine Transformation maps lines to lines.
- An Affine Transformation maps parallel lines to parallel lines.
- An Affine Transformation preserves ratios of distance along a line.
- An Affine Transformation does not preserve absolute distances and angles.
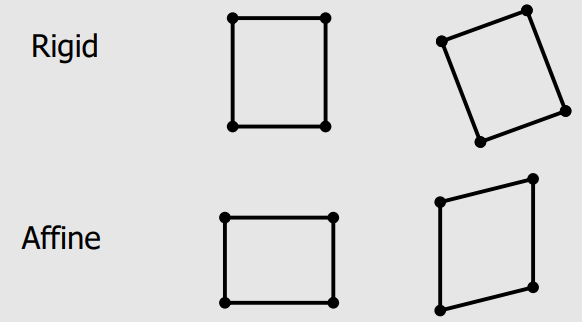
③ Rigid Transformation(강체 변환)
| 2D Spaces |
 |
| 3D Spaces |
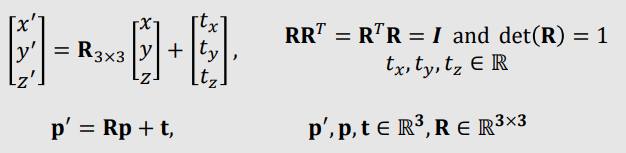 |
- A Rigid Transformation $\mathbb{T}$ is a mapping between affine spaces.
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors, and points to points.
- $\mathbb{T}: v → v', $ $v, v' \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$
- $\mathbb{T}:p → p', $ $p, p' \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$
- $\mathbb{T}$ preserves distances between all points.
- $\mathbb{T}$ cross product for all vectors (to avoid reflection)
- $\mathbb{T}$ is a function that maps vectors to vectors, and points to points.
Rigid Body Rotation
- Rigid body transformations allow only rotation and translation.
- Rotation matrics from $SO(3)$
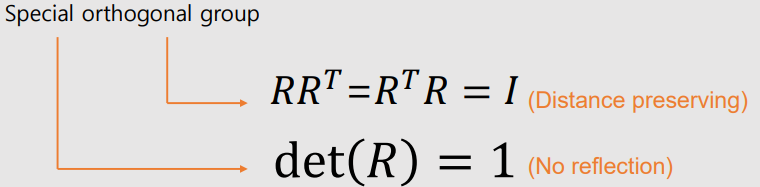
Taxonomy(분류) of Transformations
Composite Transformation(합성 변환)
Functionalization
| Translation |
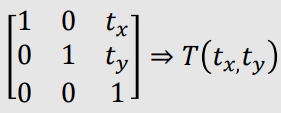 |
| Scaling |
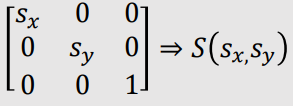 |
| Rotation |
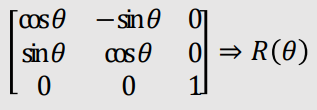 |
Composite Transformations
| Composite 2D Translation |
 |
| Composite 2D Scaling |
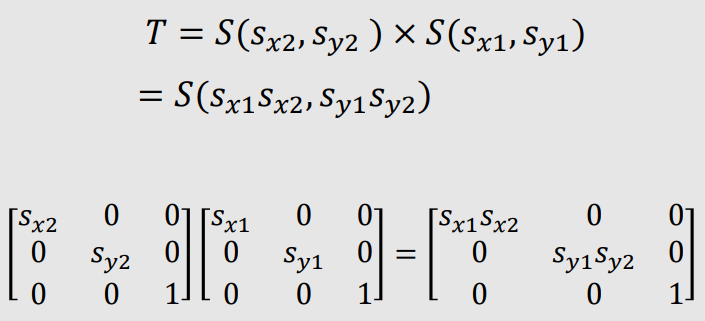 |
| Composite 2D Rotation |
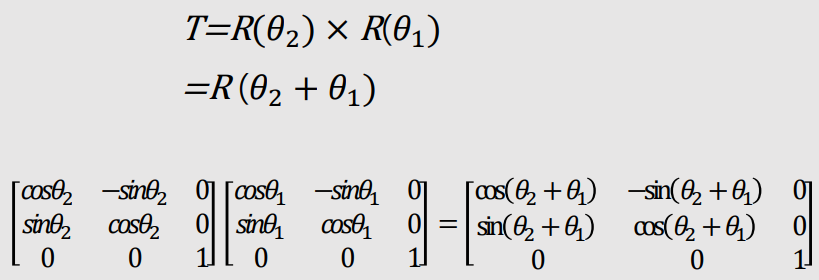 |
- Suppose we want,
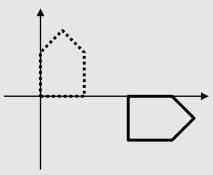
- We have to compose two transformations.
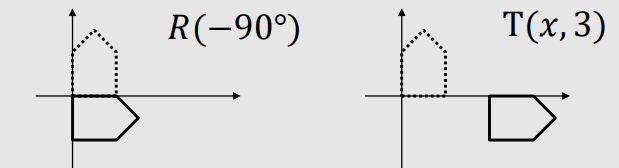
- Matrix Multiplication is not commutative(가환성의, 제시된 수의 순서에 상관 없이 결과가 동일한)
- $T(x, 3) × R(-90˚) ≠ R(-90˚) × T(x, 3)$
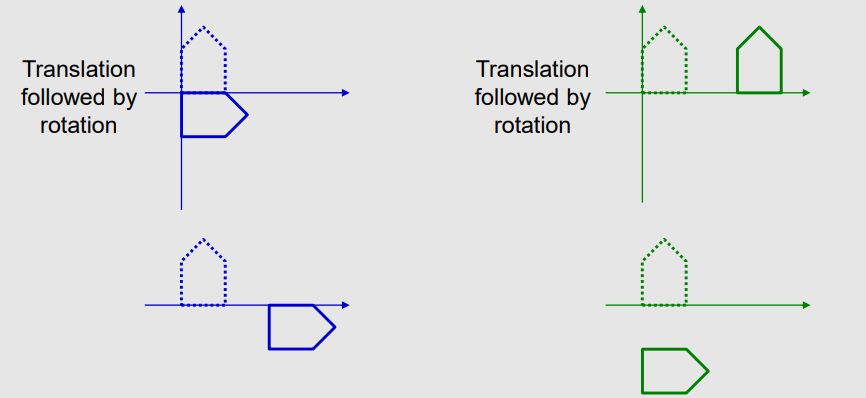
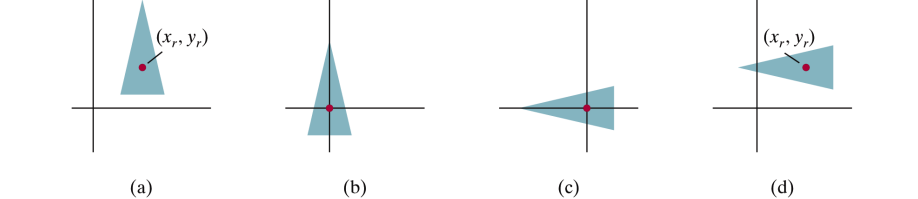
Pivot-Point Rotation
- Rotation with respect to a pivot point (x, y)
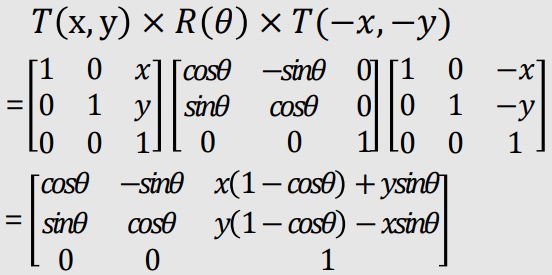
Fixed-Point Scaling
- Scaling with respect to a fixed point (x, y)
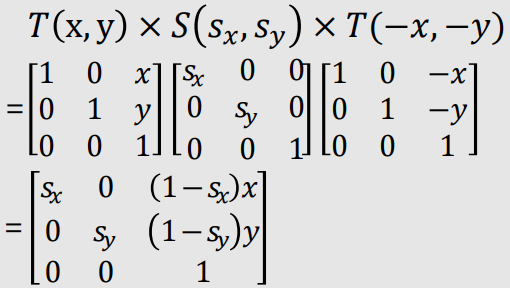
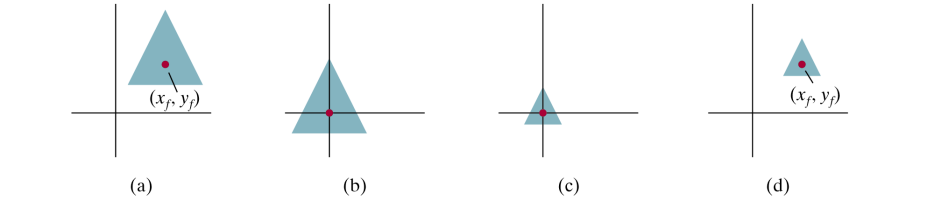
Scaling Direction
- Scaling along an arbitrary axis

728x90
'Computer Graphics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Computer Animation] Slerp(Spherical Linear Interpolation) (0) | 2022.04.10 |
|---|---|
| [Computer Animation] 3D Rotation and Orientation (0) | 2022.04.10 |
| [Computer Animation] 2D Rotation and Orientation (0) | 2022.04.03 |
| [Computer Animation] Linear Interpolation (0) | 2022.03.26 |
| [Computer Animation] Vector Operations (0) | 2022.03.15 |
| [Computer Animation] Point and Vector (Affine Geometry) (0) | 2022.03.15 |
| [Computer Animation] History of Animation (0) | 2022.03.08 |
| [Computer Animation] Computer Animation (0) | 2022.03.03 |